When it comes to sustainable eating, the future of food production is a topic that resonates with me deeply. As I delve into the realm of sustainable food practices, I am constantly amazed by the innovative solutions being developed to address the challenges our food system faces. From farm-to-table initiatives to plant-based alternatives, the landscape of food production is evolving in exciting ways.
In this article, I’ll explore the significance of sustainable eating and how it is shaping the future of food production. By adopting sustainable practices, we not only nurture our bodies but also take care of the planet. Join me on this journey as we uncover the potential impact of sustainable eating on our health, the environment, and the global food supply. Let’s discover together how small changes in our eating habits can lead to a more sustainable and resilient food future.
Importance of Sustainable Eating
Exploring the significance of sustainable eating unveils a transformative approach to food consumption. It revolutionizes our food production practices, fostering a healthier ecosystem and a more secure global food supply. Embracing sustainable eating isn’t merely a trend but a fundamental shift towards safeguarding our well-being and the Earth’s welfare.
Acknowledging the crucial role sustainable eating plays in shaping the future of food production illuminates the path to a more resilient and nourishing world. It not only enhances personal health but also contributes significantly to environmental conservation and the mitigation of climate change impacts.
By prioritizing sustainable food choices, we actively participate in safeguarding biodiversity, reducing carbon footprints, and promoting ethical food production methods. Our collective actions in choosing sustainable options ripple across the food industry, influencing supply chains to become more environmentally conscious and socially responsible.
Understanding the essence of sustainable eating empowers individuals to make informed decisions that resonate with their values and priorities. It underscores the interconnectedness between our dietary choices and broader global challenges, inspiring a holistic approach to nourishment that benefits not only ourselves but also future generations.
Benefits of Sustainable Food Production
Sustainable food production offers a host of advantages that extend beyond individual choices. Let’s dive into the key benefits of embracing sustainable eating practices.
- Environmental Impact
Reducing carbon emissions and minimizing waste are core facets of sustainable food production. By implementing eco-friendly farming methods and emphasizing local produce, we can significantly lower the environmental footprint of our food. The emphasis on biodiversity and conservation in sustainable agriculture helps protect our ecosystems and preserve natural resources for future generations. - Health and Nutrition
Choosing sustainably produced foods not only benefits the planet but also enhances our health and well-being. By opting for organic, locally sourced ingredients, we reduce exposure to harmful chemicals and pesticides. These practices promote nutritious food options, supporting a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals. Prioritizing sustainable food production aligns with a holistic approach to wellness, ensuring that we nourish our bodies while safeguarding the environment.
Challenges in Transitioning to Sustainable Food Practices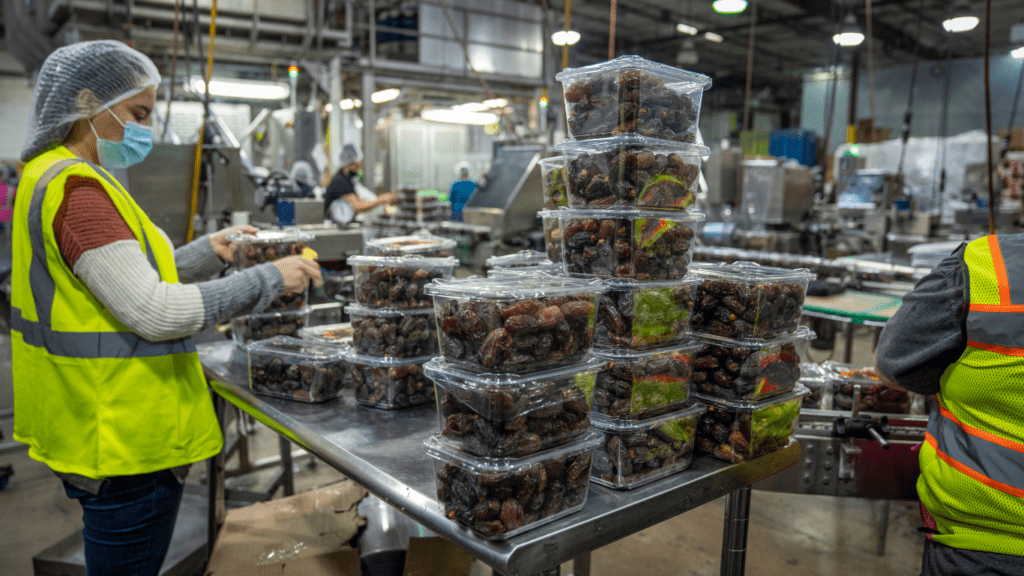
Transitioning to sustainable food practices poses various challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption and positive impact. Embracing sustainability in food production requires a shift in mindset and practices, which may face resistance due to existing systems and entrenched norms. However, overcoming these challenges is crucial for the long-term health of both individuals and the planet.
Cost Concerns
Transitioning to sustainable food practices can be perceived as costly initially. Organic produce and ethically sourced foods may have a higher price point, making them less accessible to some populations. Finding ways to make sustainable options more affordable and cost-effective is essential for encouraging broader adoption.
Supply Chain Complexity
The intricacies of sustainable food supply chains present logistical challenges. Ensuring that products are sourced ethically, transported efficiently, and reach consumers in a timely manner requires careful planning and coordination. Streamlining supply chain processes is vital for maintaining the integrity of sustainable practices.
Educational Hurdles
Many individuals may lack awareness or understanding of sustainable food practices. Educating consumers about the benefits of sustainable eating, how to identify sustainable products, and the importance of supporting eco-friendly initiatives is key to driving change. Increasing public knowledge can empower consumers to make informed choices.
Policy and Regulation
In some cases, existing policies and regulations may not fully support or incentivize sustainable food production. Governments and regulatory bodies play a critical role in creating frameworks that promote sustainable practices, such as providing subsidies for eco-friendly farming methods and enforcing environmental standards across the food industry.
Cultural Perceptions
Cultural preferences and traditions can also present challenges to transitioning to sustainable food practices. Encouraging cultural shifts towards valuing locally sourced ingredients, seasonal produce, and plant-based diets may require addressing deep-rooted culinary traditions and societal norms. Respecting diverse food cultures while promoting sustainability is essential for fostering positive change.
Addressing these challenges in transitioning to sustainable food practices involves a collective effort from individuals, communities, businesses, and policymakers. By recognizing and overcoming these obstacles, we can create a more sustainable food system that benefits both present and future generations.
Innovations in Sustainable Agriculture
Exploring innovations in sustainable agriculture reveals promising advancements transforming the future of food production. Vertical farming is a cutting-edge technique utilizing stacked layers to grow crops indoors with controlled environments. These vertical farms optimize space, reduce water usage by up to 95%, and minimize transportation costs by locating farms closer to urban centers.
Precision agriculture is another groundbreaking approach that utilizes technology like drones, GPS, and sensors to enhance farming practices. By precisely managing resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides, farmers can increase efficiency, reduce waste, and improve crop yields significantly. This technological revolution in agriculture is revolutionizing how we grow food sustainably.
Moreover, hydroponics and aquaponics are innovative methods gaining traction in sustainable agriculture. Hydroponics involves growing plants in water with added nutrients, eliminating the need for soil and reducing water usage, while aquaponics combines aquaculture with hydroponics, creating a symbiotic ecosystem where fish waste fertilizes plants. These techniques promote efficient resource utilization and environmentally friendly farming practices.
Biotechnology is playing a pivotal role in sustainable agriculture by developing genetically modified crops that are pest-resistant, drought-tolerant, and higher yielding. By harnessing genetic engineering, scientists can create crops that require fewer chemical inputs, thus reducing the environmental impact of agriculture while ensuring food security in a changing climate.
Embracing these innovative practices in sustainable agriculture is essential for addressing the challenges of food production sustainability. By adopting technological advancements, rethinking traditional farming methods, and promoting eco-friendly approaches, we can pave the way for a more resilient and sustainable food system for future generations.

Mary Norton
About the author:
Mary Norton is a key contributor at My Nutritional Balance Guide, renowned for her insightful articles and creative approach to health and nutrition topics. Learn more